
EATING
Down for the count

Counting carbs is a start, but the glycemic index (GI) is your key to a well‑balanced meal with diabetes.
Being aware of the amount of carbohydratesCarbohydrateCarbohydrates are the main kinds of food that raise blood glucose levels. Your digestive system changes carbohydrates into glucose, and then uses this glucose as a source of energy for your cells.
There are 3 main types of carbohydrates in food: starches (complex carbohydrates), sugars (simple carbohydrates), and fiber. Fiber is the part of plant foods, including fruits, vegetables, and nuts, that you can’t digest. (carbs) you eat is very important. But not all carbs are created equal. Some carbohydrate-containing foods can cause a faster rise in blood glucoseBlood glucoseThe main sugar found in the blood, and the body’s main source of energy. levels than other foods. So, counting carbs alone may not give you all the info you need. Something called the glycemic indexGlycemic index (GI)A ranking of carbohydrate-containing foods based on the food’s effect on blood glucose when compared with a standard reference food. Foods with a high glycemic index raise blood glucose more rapidly than foods with a medium or low glycemic index. (GI) can help.
What is the glycemic index?
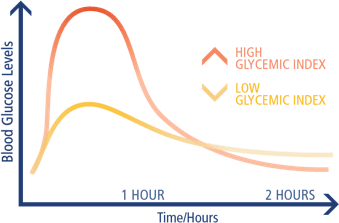
The glycemic index is a measurement of how much one kind of food will raise blood glucose levels. The theory is that a food with a low glycemic index will cause a small and slow rise in blood glucose levels, while a food with a high glycemic index will cause blood glucose to rise more quickly.
How does the glycemic index work?
The GI is based on glucose, the carbohydrate that raises blood sugar the fastest. Glucose gets the “all the way” score of 100 on the index. Other foods are then ranked on how they compare to glucose. They’re then divided into 3 levels:
- High GI
- Medium GI
- Low GI

High GI foods have a GI of 70 or more. Some examples are:
- White bread
- Potatoes (boiled)
- White rice (boiled)
- Glucose (sugar)

Intermediate or medium GI foods have a GI between 56 and 69. Some examples are:
- Honey
- Sweet potatoes (boiled)
- Pineapple (raw)
- Potato chips

Low GI foods have a GI of 55 or less. Some examples are:
- Mixed-grain breads
- Legumes (such as chickpeas, beans, and lentils)
- Milk and yogurt
- Ice cream
Other things to keep in mind when using the glycemic index
- The GI shows what type of carb a food contains. But it can’t tell you how many carbs are being eaten. So, you still have to think about portion size
- Mixing foods with different GIs may help balance out their effect on blood glucose
- Foods that are good for you can still have a high GI. And foods with little nutrition may also have a low GI. For example, chocolate has a fairly low GI (40), and so does ice cream (51). But their high saturated fat content reduces their nutritional value even though meals with fat are converted more slowly into blood glucose
- While the GI can help you compare or rank food choices, not everyone agrees how helpful it is for blood glucose control. So, before changing what you eat based on the GI, talk to your doctor about how it may (or may not) help your diabetes care plan
Test your knowledge
The glycemic index measures how many carbs you’re eating.
Correct!
Sorry, that's incorrect.
The GI only measures what type of carbs a food has, not how much. So, you still have to watch your serving size.



