MOVING
How active is active enough?

Finding the right activity plan if you have type 1 diabetes.
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) says that children with type 1 diabetes should have at least 1 hour of physical activity each day. Adults aren't off the hook either. The ADA says that adults with type 1 diabetes should get 150 minutes or more of moderate-to-vigorous aerobic activity per week, spread over at least 3 days. So, no going more than 2 days in a row without being active!
Of course, some people may have physical issues that make it hard to move so much. But you owe it to yourself to speak with your diabetes care teamDiabetes care teamYour diabetes care team may include a primary care doctor, a diabetes and hormone doctor (endocrinologist), a registered nurse, a diabetes educator, a dietitian, a heart doctor (cardiologist), a foot doctor (podiatrist), an eye doctor (ophthalmologist/optometrist), a kidney doctor (nephrologist), a dentist, a pharmacist, and a mental health professional. about safe ways to be as active as you can. There are also some important steps for you to take to help keep your blood glucoseBlood glucoseThe main sugar found in the blood, and the body’s main source of energy. and other diabetes issues under control when you get active.
Walking is an ideal way to get started
Not a jock? Don’t like team sports? Don’t worry. There are lots of other fun ways to be active, such as walking or dancing. Walking can be a great way to get moving, especially if you’re not used to being very active.
Why walk?
- It can fit into most days. Try doing errands on foot rather than taking the car—especially if you’re in an area where shops are located nearby
- It’s cheap. Got a pair of comfy sneakers or walking shoes? That’s all you need to start walking! No? Then go out and get a pair! You don’t need to have pricey athletic shoes—just ones that fit comfortably
- It can be adjusted to work with your current fitness level. Just getting started? A walk around the block is fine. Want more of a challenge? Find a large park with some hills
- It’s heart healthy. Walking even 30 minutes a day, 5 times a week can help the heart and lungs
- It’s a great way to go places. Walking may take a little longer than driving or taking a bus. But it also lets you slow down and really see things. It saves money and is good for the environment too!
An experienced walker can walk 1 mile in 10 to 12 minutes. A pace of 4 miles per hour (or 15 minutes per mile) is a good goal to work toward. If you’re not used to walking, it may take a while to get that fast. At first, it may take 30 minutes to walk a mile, but that’s okay. Enjoy it!

Customize your activity plan
Your diabetes care team can help you create a physical activity plan that’s safe and comfortable. As you get more fit, the plan will need to be freshened up to keep it both interesting and challenging.
Testing blood glucose
Nearly any activity lasting 30 minutes or more will affect blood glucose. That’s why you should check blood glucose before, during, and after being active. From this, you can learn how certain activities affect your blood glucose.
Before exercise – always test blood glucose levels before exercise
- If the blood glucose reading is less than 100 mg/dL, you may need an extra carbohydrateCarbohydrateCarbohydrates are the main kinds of food that raise blood glucose levels. Your digestive system changes carbohydrates into glucose, and then uses this glucose as a source of energy for your cells.
There are 3 main types of carbohydrates in food: starches (complex carbohydrates), sugars (simple carbohydrates), and fiber. Fiber is the part of plant foods, including fruits, vegetables, and nuts, that you can’t digest. snack, such as a piece of fruit or a few crackers. Then test 15 to 30 minutes later. Don’t start exercising until your blood glucose is above 100 mg/dL
- Do NOT exercise when your urine tests show ketonesKetonesOrganic compounds produced when the body breaks down fats and fatty acids to use as fuel. This is most likely to occur when the body does not have enough glucose or carbohydrates or the body cannot use glucose effectively. Because high levels of ketones are dangerous, a urine test is one way to check the level of ketones in your body. and your blood glucose is high. High levels of ketones and high blood glucose levels can mean your diabetes is out of control. Check with your doctor about how to handle this situation
- If the blood glucose reading is less than 300 mg/dL and there are no ketones present, then it is okay to exercise with caution. But keep checking blood glucose during exercise
During exercise – it may be necessary to test during activity, especially if you’re exercising for a long time. A snack may be needed during exercise if blood glucose levels are low
After exercise – exercise generally (but not always) lowers blood glucose, so it is a good idea to test afterwards, too. Blood glucose levels can go too low if you exercise for long periods or on an empty stomach
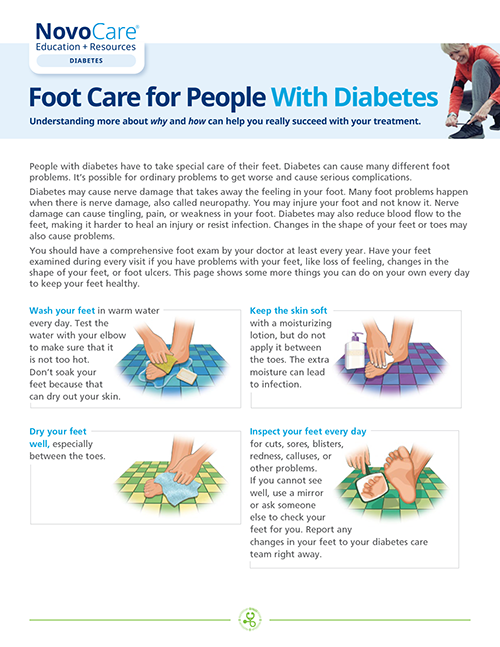
Remember to keep an eye on your feet! Download foot care for people with diabetes
Test your knowledge
What’s one thing you should always have with you when you go for a long walk?
Correct!
Sorry, that's incorrect.
It’s smart to have a fast-acting carbohydrate snack or drink on hand if you start to feel like you have low blood glucose (hypoglycemia) during physical activity. You should stop what you’re doing and have a sports drink, fruit juice, glucose tablet, or hard candy before you resume.