STAYING ON TRACK
High blood glucose: What you need to know

Learn the signs of hyperglycemia and how to help manage it.
High blood glucose, or hyperglycemia, happens when the amount of glucose in your blood rises to 180 mg/dL or higher after meals. High blood glucose may affect people whether their diabetes is well controlled or not. In people whose diabetes is not well controlled, episodes of high blood glucose may happen because they are not treating their diabetes properly. Or they may not even know that they have diabetes. For people who use an insulin pump, blocked tubing could also lead to high blood glucose. If left untreated, high blood glucose can cause serious health problems.
How high is high? How to measure if your blood glucose is high.
What causes high blood glucose?

High blood glucose can happen if you:
- Skip a dose of medicine
- Eat more than usual
- Are less active than usual
- Feel stressed
- Are sick
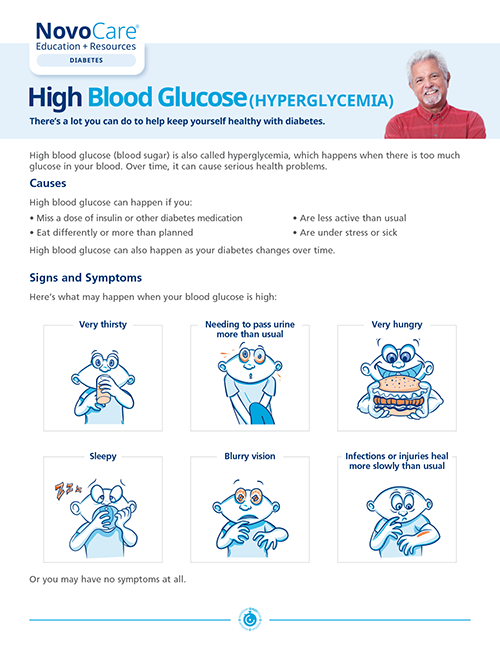
The symptoms of high blood glucose
It’s important to recognize the signs and symptoms of high blood glucose early, so something can be done before it gets worse.
You may have high blood glucose if you:
- Feel very thirsty or hungry
- Need to pass urine more often
- Feel like your mouth and skin are dry
- Have blurry eyesight
- Feel tired or weak
- Notice that sores and wounds are healing slower than usual
- Have unexplained weight loss
What to do about high blood glucose
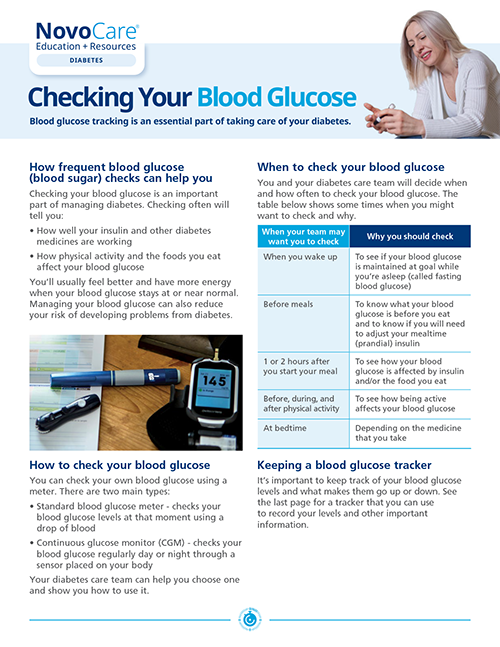
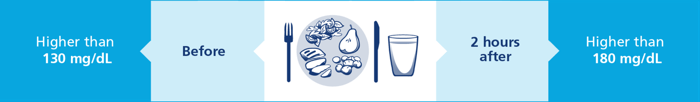
If you have signs or symptoms of high blood glucose (higher than 130 mg/dL before a meal or higher than 180 mg/dL 2 hours after starting a meal), follow these steps:

- Drink plenty of water or sugar-free fluid. Try to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day
- Check your blood glucose more often. Check before meals, at bedtime, and occasionally 2 hours after a meal
- Look for patterns. Track the times and potential causes of high blood glucose readings and share any patterns you see with your doctor
- Always follow the advice of your doctor. Your doctor and diabetes care team can help you stay on track
If your blood glucose is higher than usual, you can help lower it if you:
- Follow your meal plan
- Follow the activity plan you have discussed with your diabetes care team
- Take your medicine at the right time
Download Checking your blood glucose
You can also ask your health care provider about a continuous glucose monitor, which can track your glucose in real-time. A better understanding of your blood glucose can help you achieve a longer time-in-range.
High blood glucose can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA, in people who have type 1 diabetes (it’s very rare for type 2). DKA happens when there is a buildup of ketonesKetonesOrganic compounds produced when the body breaks down fats and fatty acids to use as fuel. This is most likely to occur when the body does not have enough glucose or carbohydrates or the body cannot use glucose effectively. Because high levels of ketones are dangerous, a urine test is one way to check the level of ketones in your body. in the blood. Ketones are made when the body uses fat for energy instead of glucose. This can happen when the cells don’t get the glucose they need to use for energy.
Symptoms of DKA that may require ketone testing include:
- Blood glucose above 240 mg/dL and not falling
- Intense thirst or dry mouth
- Need to urinate often
- Lack of appetite, or stomach pain
- Vomiting or nausea
- Blurry vision
- Fever or warm, dry, or flushed skin
- Difficulty breathing
- Feeling weak
- Sleepiness
- Fruity odor on the breath
How to test for ketones
- Over-the-counter test strips are used to measure the amount of ketones in the urine. These strips are available without a prescription in most local pharmacies
- Some blood glucose meters also check for ketones in the blood
What level of ketones is considered dangerous?
Your diabetes care teamDiabetes care teamYour diabetes care team may include a primary care doctor, a diabetes and hormone doctor (endocrinologist), a registered nurse, a diabetes educator, a dietitian, a heart doctor (cardiologist), a foot doctor (podiatrist), an eye doctor (ophthalmologist/optometrist), a kidney doctor (nephrologist), a dentist, a pharmacist, and a mental health professional. will often tell you what level of ketones is dangerous. If they have not, call your doctor if a urine test shows moderate or large amounts of ketones.
What is the most important information I should know about ketones?
- Test for ketones every 4 hours during illness. DKA can be common when people with type 1 diabetes are sick. Even if blood glucose tests are normal, if you’re nauseous or vomiting, check your urine for ketones
- Seek emergency help if ketones do not go down, or if you’re vomiting and cannot stop
- Avoid activity when ketones are elevated and blood glucose is high
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome, or HHS, is a severe condition. It happens when high blood glucose levels cause an unusual increase in urination. This can lead to dehydration.
If your blood glucose levels are running high, but you don’t know why, you may need medical attention. Your doctor can tell you what blood glucose levels and symptoms are associated with HHS and when you should call someone from your diabetes care team if you experience them.
What are common reasons you should call your doctor?
- Your blood glucose goes above your goal for more than 2 test results
- You feel ill, have a fever, feel sick to your stomach, or are vomiting
- You are scheduled to have surgery or have recently had surgery
- You have any questions about what blood sugar levels are too low or too high